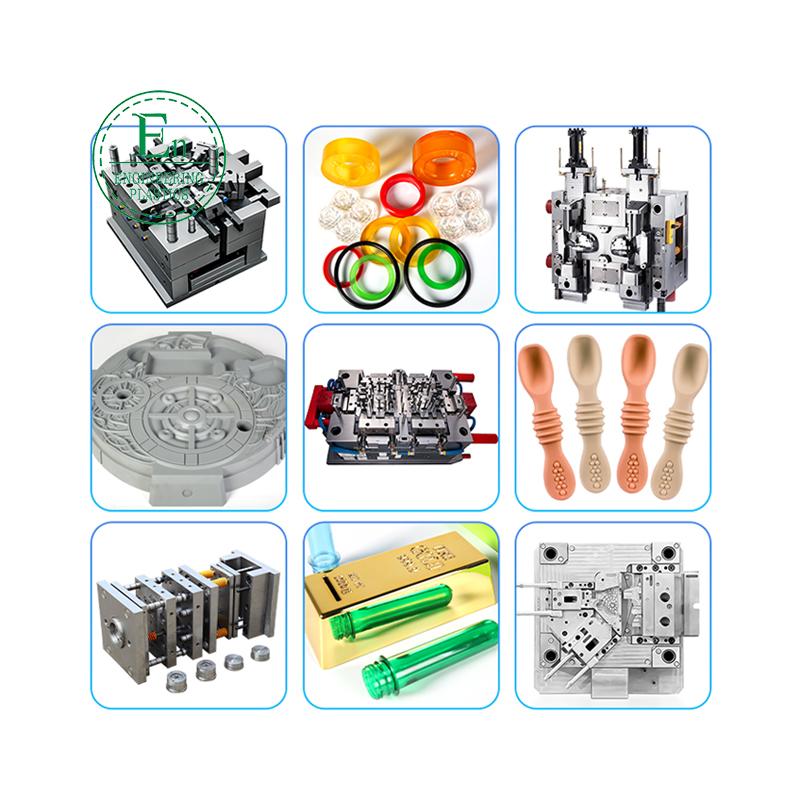
We’re Guangdong Engineering Plastics Industries Group Co., Ltd. , a specialized manufacturer of custom molds and injection molding solutions with 26 years of experience serving global clients.
Our expertise includes:
*Complex Mold Design: Multi-cavity, hot-runner, and micro-molding capabilities
*Full-Service Production: From prototyping to high-volume manufacturing
*Material Options: Engineering plastics, LSR, biodegradable polymers, etc.
*Quality Assurance: ISO 9001-certified with strict tolerance control (±0.01mm)
We’ve successfully delivered projects for industries including aerospace, automotive, robotics , and medical devices.
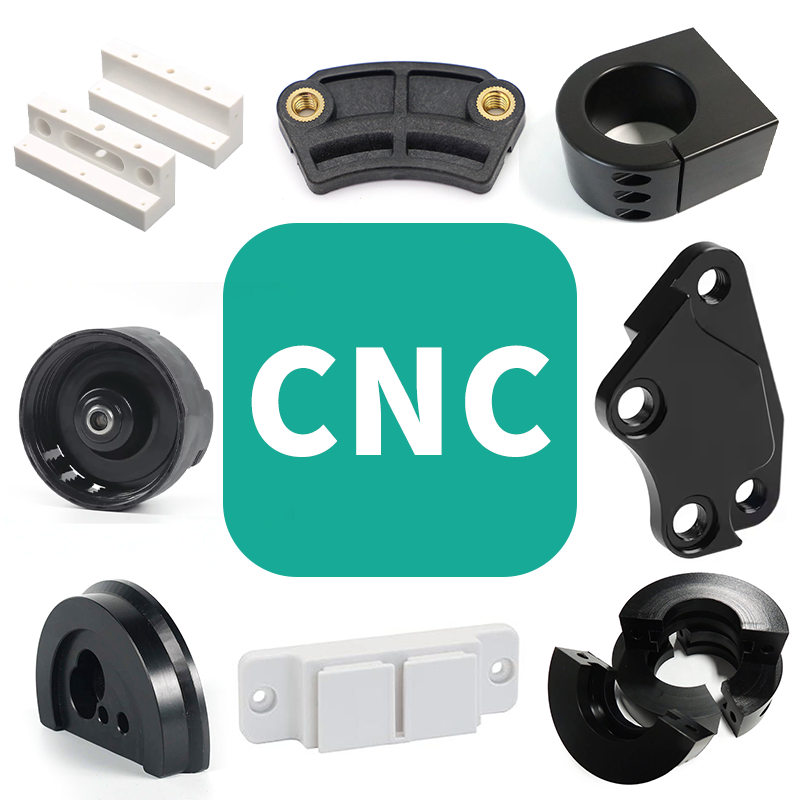
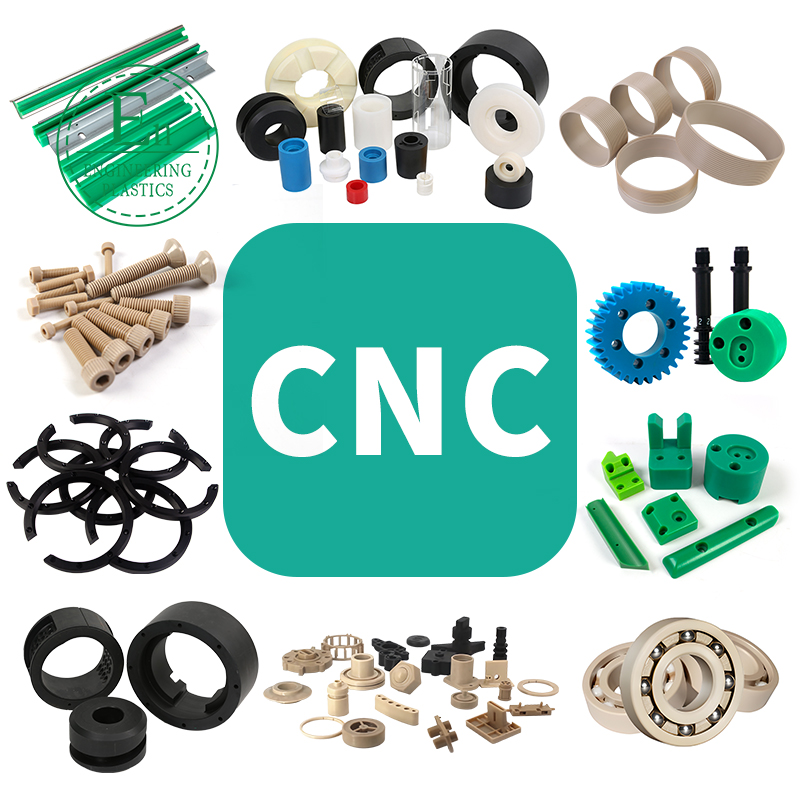
Our factory specializes in high-accuracy CNC machining of plastic components, utilizing state-of-the-art computer numerical control technology to deliver exceptional dimensional consistency and complex geometries. We process a wide range of engineering-grade thermoplastics including PEEK, PPS ,PAI, PI, PBI,PTFE,Nylon, ABS, POM, UHMWPE, PE,PSF, PEI, PSU, etc, catering to industries requiring tight tolerances from automotive to medical applications.
Could we schedule a call to discuss how we can optimize your next project for quality, cost, and lead time?
Email:sales@gz-plastics.com
Tel: +8618588927610
Website:https://gz-plastics.com/
In the world of modern manufacturing, the ability to produce large quantities of identical, high-quality parts efficiently is paramount. Central to achieving this is the process of injection molding, a highly versatile and widely used manufacturing technique for creating plastic components. This technology has revolutionized countless industries by enabling the mass production of complex parts with incredible precision and speed, making it a cornerstone of how we create everything from simple consumer goods to critical automotive and medical components.
The Critical Role of Injection Molds
At the very core of this entire process are the injection molds themselves. A mold is not just a simple container; it is a highly engineered, custom-built tool, typically made from hardened steel or aluminum, that dictates the final shape and finish of the plastic part. The creation of high-quality injection molds is a meticulous process involving computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) to create two halves of a tool—the cavity and the core. The precision of these molds is critical, as any imperfection will be directly replicated on every part produced. The quality, durability, and design of the injection molds ultimately determine the success and efficiency of the production run.
Demystifying the Plastic Injection Molding Process
The plastic injection molding process is a cycle that can be broken down into several key stages. First, small plastic pellets are fed into a hopper, which directs them into a heated barrel. A reciprocating screw within the barrel melts and homogenizes the plastic, preparing it for injection. Once the material is at the correct temperature and consistency, the two halves of the mold are clamped together with immense force. The molten plastic is then injected under high pressure into the mold cavity, filling it completely. After the injection phase, the part is allowed to cool and solidify within the mold. Finally, the mold opens, and ejector pins push the finished part out, readying the machine for the next cycle. This entire sequence can take just a few seconds, allowing for extremely high output.
Advantages and Applications
The benefits of injection molding are numerous, making it the preferred method for many applications. Its primary advantage is scalability; while the initial investment in tooling (the injection molds) can be significant, the cost per part becomes extremely low when producing thousands or millions of units. The process also offers exceptional design flexibility, allowing for the creation of intricate and complex geometries that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with other manufacturing methods. Furthermore, plastic injection molding is known for its high repeatability, ensuring that every part is virtually identical to the last. This technology is used across a vast spectrum of industries, including automotive for creating dashboards and bumpers, medical for producing syringes and device housings, electronics for casings, and consumer goods for everything from toys to kitchen utensils.